B It has two sites. Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products protein or non-coding RNA and ultimately affect a phenotype as the final effectThese products are often proteins but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA tRNA and small nuclear RNA snRNA the.
What Is The Anticodon Of Trna Molecules Quora
TRNAs are enzymatically modified post-transcriptionally.
. Transfer RNA tRNA is an adapter molecule that links a specific codon in mRNA with its corresponding amino acid during protein synthesis. When the tRNA recognises its complementary codon in the mRNA strand it goes to collects its. A It represents a single amino acid to which it binds covalently.
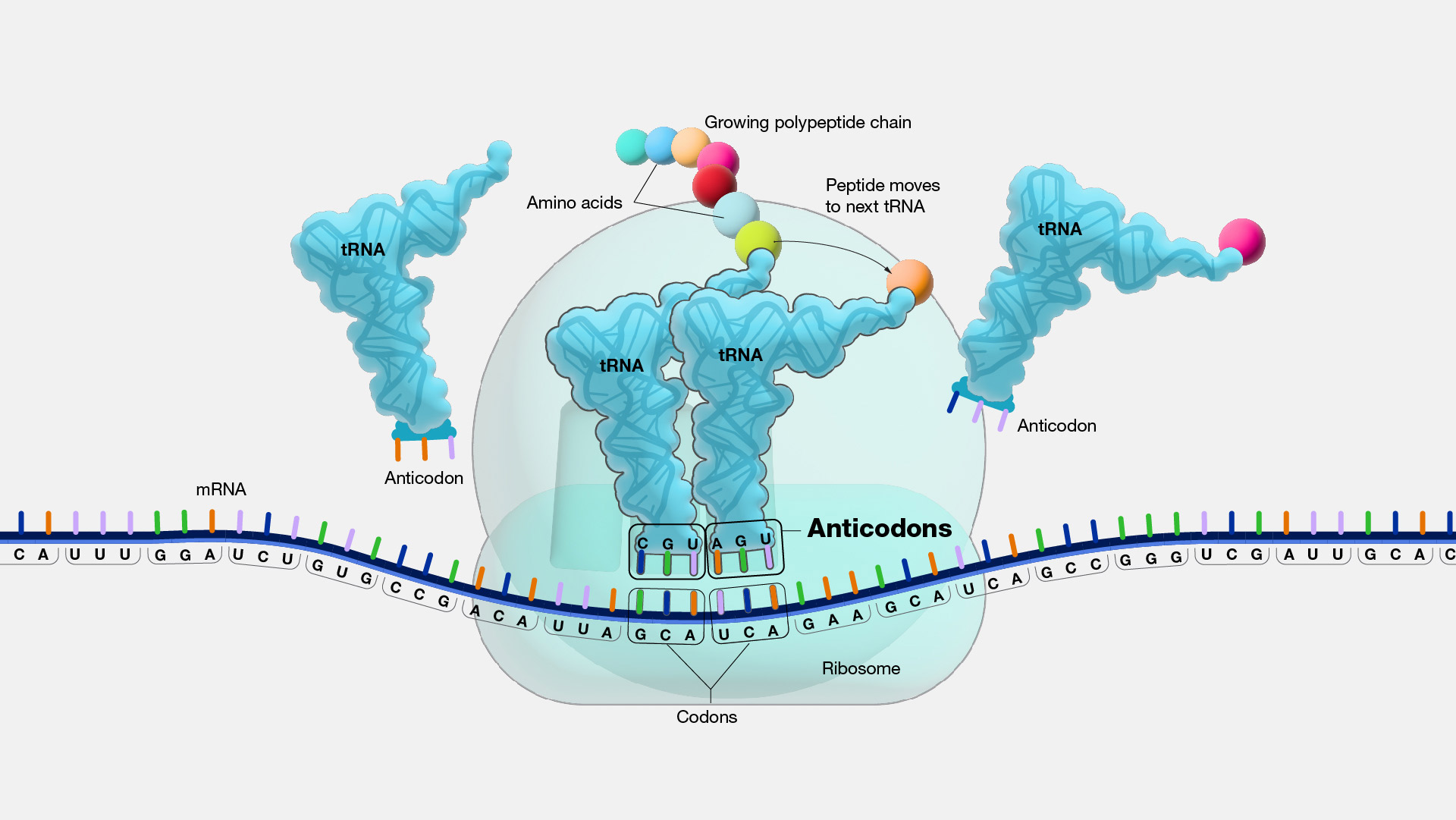
The three bases of the tRNA molecule are known as an anticodon. One is a trinucleotide sequence called anticodon which is complementary to the codon of mRNA. There are various different kinds of transfer RNA tRNA.
In this configuration uracil is sometimes referred to as pseudouracil Pseudouridine is the most abundant RNA modification in cellular RNA. As a result aminoacyl-tRNA AMP and enzyme are formed. TRNA molecules fold into a similar stem-loop arrangement which resembles a cloverleaf in two dimensions.
On the other end of the transfer RNA tRNA the amino acid present to specified by the codons. See the figure below. Each kind of transfer RNA read one or.
During the translation process the Anticodon bases form corresponding base sets among the bases of. The transfer of aminoacids to tRNA is catalysed by the previous aminoacyl RNA synthetase enzyme itself Fig. When the correct tRNA finds the mRNA its amino acid is added to the growing protein chain.
The opposite end of the tRNA molecule has a site where a specific amino acid can bind to. The codon and anticodon form. There is one aminoacyl tRNA synthetase for each of the 20 amino acids and the enzyme can recognize all the anticodons that represent that particular amino acid.
Enzymes catalyze the bonding of amino acids together as tRNA anticodons bind to the correct mRNA codon. A transfer RNA molecule can enter the ribosome guaranteed to an organic compound. These enzymes use the energy from ATP to attach the.
Pseudouridine abbreviated by the Greek letter psi- Ψ is an isomer of the nucleoside uridine in which the uracil is attached via a carbon-carbon instead of a nitrogen-carbon glycosidic bond. Normally only the correct codonanticodon pairing is recognised and the bound tRNA is stabilised by two unpaired 16S rRNA bases A1492 and A1493 flipping their orientation. The anticodon can base pair with its corresponding codon or codons in mRNA.
Anticodons are basically the section of a transfer RNA t RNA is a categorization of three bases which are corresponding to codons in the mRNA. An anticodon is a trinucleotide sequence located at one end of a transfer RNA tRNA molecule which is complementary to a corresponding codon in a messenger RNA mRNA sequence. For example an mRNA codon with bases UGU would have a complementary tRNA with an anticodon AGA.
When the tRNAs amino acid has been added to the protein chain the tRNA leaves to pick up a new amino acid to bring to a new mRNA. The tRNA plays the role of an adaptor and matches each codon to its particular amino acid in the cytopolasmic pool. After transcription and following synthesis RNA.
Each mature tRNA contains an average of 13 such modifications per molecule. A codon is a DNA or RNA sequence of three nucleotides a trinucleotide that forms a unit of genetic information encoding a particular amino acid. Each time an amino.
A group of enzymes called aminoacyl tRNA synthetases attach the appropriate amino acid to tRNA molecules based on their anticodon. C The aminoacids tRNA complex then comes to mRNA where adapter nucleotide triplet or anticodon of tRNA becomes attached with the complementary base triplet codon of mRNA. Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase aaRS enzymes then charge each mature tRNA with an amino acid on their 3 end a process.
Each transfer RNA or tRNA has a sequence of three nucleotides at the one end known as Anticodon that can bind to particular mRNA codons. The tRNA has two properties. Its structure has an acceptor arm for attachment of specific amino acids and a stem loop with a three-base anticodon sequence at its ends.
When an aminoglycoside is bound non-cognate pairing is tolerated particularly at base 1 of the codon such that codonanticodon pairings with one mismatch occur and the flipping of the unpaired.

Anticodon An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
What Is The Anticodon Of Trna Molecules Quora

Solved 21 The Anticodon Of A Particular Trna Molecule Is Complementary To The Corresponding Triplet In Rrna Complementary To The Corresponding Mrna Codon The Part Of Trna That Bonds To A Specific
0 Comments